دوشنبه سی ام مهر ۱۴۰۳ - 1:29 - با امید -
Join usSign in
Forum Institutional
5 ways governments can unlock a more social economy
May 23, 2022
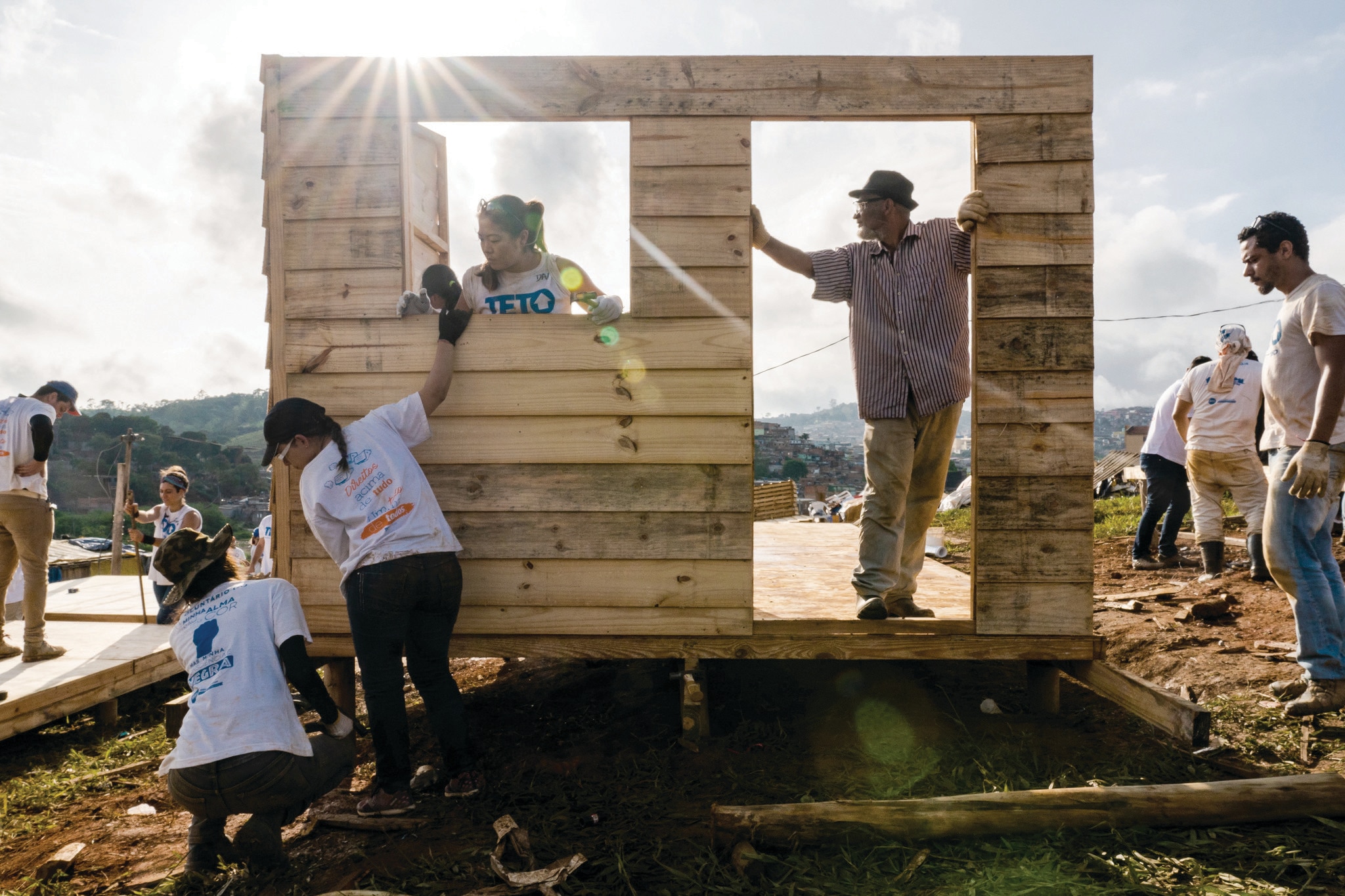

A United Nations report estimates that the social economy accounts for around 7% of global GDP.
Image: Editora Mol.
Johanna Mair
Professor of Organization, Strategy and Leadership, Hertie School and Stanford University
Jonathan Wong
Chief of Innovation, Enterprise and Investment, United Nations Economic and Social Commission for Asia and the Pacific (UNESCAP)
Precious Moloi-Motsepe
Co-Founder and Chief Executive Officer, Motsepe Foundation
Francois Bonnici
Director, Schwab Foundation for Social Entrepreneurship; Head of Foundations, World Economic Forum
Share:
Our Impact
What's the World Economic Forum doing to accelerate action on Forum Institutional?

The Big Picture
Explore and monitor how Social Innovation is affecting economies, industries and global issues

Crowdsource Innovation
Get involved with our crowdsourced digital platform to deliver impact at scale
Stay up to date:
Davos Agenda
Follow
This article is part of:World Economic Forum Annual Meeting
Listen to the article
11 min listen
- In the EU alone, there are 2.8 million social economy organizations, employing 13.6 million people, representing up to 9.9% employment in some countries.
- The social economy supports disadvantaged groups, drives sustainable development and offers an alternative to our current economic model.
- A new report, Unlocking the Social Economy, from the World Economic Forum, provides five key policy recommendations to advance the sector.
The COVID-19 pandemic has been no ordinary crisis. The worst health emergency in more than a century has been compounded by growing inequality and rapidly rising food and energy prices this year. This causes structural damage to economies and people’s lives on a scale that can hardly be addressed by means of traditional approaches of fiscal and monetary stimulus.
In many countries, job losses and other hardships have been disproportionately concentrated amongst the poor, youth, and women. As a result, Oxfam reports that the total number of people in extreme poverty could rise to 860 million this year. This emphasizes the need for inclusive models of economic development that build social cohesion and address social inequalities.
Have you read?
The social innovators of 2022 are building trust and supporting millions
Transforming through Trust: How social innovators are transforming the lives of 722 million
How social 'intrapreneurs' can help businesses achieve ESG targets
Unlocking the Social Economy Towards an inclusive and resilient society
Over decades, social enterprises, cooperatives, inclusive businesses, and innovative non-profits have prioritised social and environmental value. They made a difference where it matters: on the ground, among local communities and natural ecosystems facing damage and loss. These organizations have explicit social objectives and inclusive governance models, working with groups who face barriers because of gender, race, ability and economic class.
"Thanks to its strong local roots, the social economy can offer innovative bottom-up solutions to many of the global challenges of today, such as climate change, digitization and social exclusion. The social economy works with and for local communities and has a huge job creating potential." Nicolas Schmit, European Commissioner for Jobs and Social Rights.
Unlocking the social economy
A United Nations report estimates that the social economy accounts for around 7% of global GDP and contributes to increased employment in economies. In times of multiple and interrelated challenges, social economy organizations strengthen resilient communities and help manage major transitions. In addition, employment in the social economy grew by 12-20% during the 2008 financial crisis, in contrast to the sharp job losses in the private and public sectors.

Click to enlarge
Spectrum of Social Economy Actors. Source: The World Economic Forum.
More and more governments recognize the potential of the social economy to address global challenges. This year the European Commission launched its Social Economy Action Plan; the International Labour Organization has for the first time ever tabled a discussion on it during their conference and the Organisation for Economic Cooperation and Development is making legal recommendations in this regard to its members.
But despite its potential, social economies around the globe encounter common barriers which keep them from growing: limited visibility; lack of a supportive legal and regulatory frameworks; lack of verification and standards; inadequate supply of financial resources and restricted access to markets.
The Insight Brief, Unlocking the Social Economy, outlines five concrete policy areas that governments can develop to build more inclusive, sustainable and resilient societies.
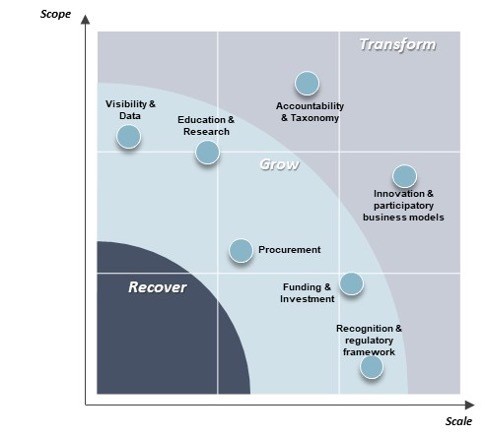
Click to enlarge
Key policy areas to unlocking the social economy. Source: The World Economic Forum.
1. Recognize and build new frameworks
The political recognition, development of regulatory environments and regular dialogue with social economy actors has proven vital in countries to grow the sector. In 2007, the Republic of Korea put in place the Social Enterprise Promotion Act to promote, incentivise and regulate social enterprises. The European Commission recently launched its 2021-2027 Social Economy Action Plan, investing over €2.5 billion to enhance social investment, support social economy actors to start up, scale-up, innovate, and create jobs.
2. Create incentives for funding and investment
Governments can grow the social economy by investing public funding and by encouraging investment by mainstream finance providers and social investors. Mechanisms include fiscal incentives, alleviating regulatory barriers, leveraging tax frameworks, de-risking private funding and developing hybrid mechanisms that blend public and private investment. The government of Singapore set up the Singapore Centre for Social Enterprise (raiSE) to offer grants to Singapore-based social enterprises to develop the sector and address human-centred social gaps in the country through the collaboration of public and private actors.
3. Expand education and research
Expanding and enhancing research and education on social innovation, social enterprise and the social economy in schools and universities can develop both the local knowledge and the talent pipeline. For example, Scotland launched the Social Enterprise in Education programme in 2007 to increase the understanding of the social economy and to promote awareness among youth and students. The programme focuses on development of and understanding for social enterprise business models and provides hands-on experience
Discover
What is the World Economic Forum doing to champion social innovation?
Show more
Accept our marketing cookies to access this content.
These cookies are currently disabled in your browser.
Accept cookies
4. Make public and private procurement channels more inclusive
The public sector can buy goods and services from enterprises that deliver social and environmental value. In this way, procurement becomes a vehicle to meet other objectives, such as reintegrating long-term unemployed into labour markets and social and work integration of people from excluded or vulnerable groups. Governments can also create incentives for the private sector to procure from the social economy. In 2014, EU member states adopted the EU public procurement rules allowing for “environmental and social considerations”, as well as innovation aspects to be taken into account when awarding public contracts.
5. Collect and make visible social impact data
To increase the visibility of the sector, governments are encouraged to collect statistics on the social economy which go beyond traditional indicators. Besides the contribution of the social economy to economic growth and job creation, governments should systematically measure and present the social and environmental impact of the social economy. The Social Progress Index measures the extent to which social needs of citizens are being fulfilled through the three dimensions: basic human needs, foundations of wellbeing and opportunity, by aggregating 35 social indicators.
A second shift towards transforming the mainstream economy
Social economy actors are often pioneering in developing social and environmental innovations. They have proven to co-develop solutions that the mainstream economy has adopted. They can bring inclusive and just contributions towards green and digital transitions by putting people at the center, and can serve as a source of inspiration for the private sector in their ESG goals.
"As social entrepreneurial models continue to be successful both from an impact and profit perspective, the private sector has increasingly started to integrate impact into their operating models, whilst still remaining profitable. As this happens, the lines between purely social enterprises and traditional enterprises that also create a social benefit are increasingly blurring, which is a good thing." Sharon Thorne, Deloitte Global Board Chair.
Through the adoption of frameworks of accountability, taxonomies of social reporting, and more participatory business and governance models, the social economy can contribute to the structural transformation of our current economic model with its persisting challenges and accelerate transitions towards a more inclusive, sustainable future.
The Insight Report, Unlocking the Social Economy, has been contributed to by a Working Group convened by the World Economic Forum’s Global Alliance for Social Entrepreneurship and the Schwab Foundation for Social Entrepreneurship, in partnership with Deloitte, Euclid Network, Catalyst 2030 and the Motsepe Foundation.
Accept our marketing cookies to access this content.
These cookies are currently disabled in your browser.
Accept cookies
Don't miss any update on this topic
Create a free account and access your personalized content collection with our latest publications and analyses.
Sign up for free
License and Republishing
World Economic Forum articles may be republished in accordance with the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International Public License, and in accordance with our Terms of Use.
The views expressed in this article are those of the author alone and not the World Economic Forum.
Related topics:
Forum InstitutionalSocial InnovationJobs and the Future of WorkEconomic Growth
Share:
 Global Agenda
Global Agenda
The Agenda Weekly
A weekly update of the most important issues driving the global agenda
Subscribe today
You can unsubscribe at any time using the link in our emails.For more details, review our privacy policy.
More on Forum Institutional
See all

Country Strategy Meeting - Argentina
Marisol Argueta de Barillas
October 20, 2024

AI value alignment: How we can align artificial intelligence with human values
Benjamin Larsen and Virginia Dignum
October 17, 2024

How digital nomads can transform tourism and the economy of Small Island Developing States
Pedro Lopes
October 17, 2024

How to “blink responsibly” on unrealistic climate goals – and set a course for action
David G. Victor and Joisa Dutra
October 17, 2024

Global Future Councils: Experts talk intelligent economies, inclusive growth, collaboration and more in Dubai
Spencer Feingold
October 16, 2024

Creating a plastic-free tourism sector is a challenge. Here's why it's worth it
Marina Novelli and Jo Hendrickx
October 16, 2024
باز کردن قفل اقتصاد اجتماعی
گزارش سازمان ملل تخمین می زند که اقتصاد اجتماعی حدود 7 درصد از تولید ناخالص داخلی جهانی را تشکیل می دهد و به افزایش اشتغال در اقتصادها کمک می کند. در زمان چالش های متعدد و به هم پیوسته، سازمان های اقتصاد اجتماعی جوامع تاب آور را تقویت می کنند و به مدیریت انتقال عمده کمک می کنند. علاوه بر این، اشتغال در اقتصاد اجتماعی در طول بحران مالی سال 2008 12 تا 20 درصد رشد کرد، در مقایسه با از دست دادن شدید شغل در بخش های خصوصی و دولتی.
دولت های بیشتری پتانسیل اقتصاد اجتماعی را برای مقابله با چالش های جهانی تشخیص می دهند. امسال کمیسیون اروپا برنامه اقدام اقتصاد اجتماعی خود را راه اندازی کرد. سازمان بین المللی کار برای اولین بار در کنفرانس خود در مورد آن بحث کرده است و سازمان همکاری و توسعه اقتصادی در این زمینه توصیه های قانونی به اعضای خود ارائه می دهد.
اما علیرغم پتانسیل آن، اقتصادهای اجتماعی در سراسر جهان با موانع مشترکی مواجه هستند که مانع از رشد آنها می شود: دید محدود. عدم وجود چارچوب های قانونی و نظارتی حمایتی؛ عدم تأیید و استانداردها؛ عرضه ناکافی منابع مالی و دسترسی محدود به بازارها.
خلاصه بینش، باز کردن قفل اقتصاد اجتماعی، پنج حوزه سیاست گذاری مشخص را تشریح می کند که دولت ها می توانند برای ایجاد جوامع فراگیرتر، پایدارتر و انعطاف پذیرتر توسعه دهند.
به ما بپیوندیدورود به برنامه
مراکز
انتشارات
رویدادها
دستور کار انجمن
هوش
فیلم
پادکست
در باره ما
Uplink
انجمن نهادی
5 راهی که دولت ها می توانند اقتصاد اجتماعی تری را باز کنند
ممکن است 23، 2022

گزارش سازمان ملل تخمین می زند که اقتصاد اجتماعی حدود 7 درصد از تولید ناخالص داخلی جهانی را تشکیل می دهد.
تصویر: Editora Mol.
یوهانا میر
استاد سازمان، استراتژی و رهبری، مدرسه هرتی و دانشگاه استنفورد
جاناتان وانگ
رئیس نوآوری، سرمایه گذاری و سرمایه گذاری، کمیسیون اقتصادی و اجتماعی سازمان ملل متحد برای آسیا و اقیانوسیه (UNESCAP)
مولوی-موتسپه گرانبها
یکی از بنیانگذاران و مدیر اجرایی، بنیاد موتسپه
فرانسوا بونیچی
مدیر بنیاد شواب برای کارآفرینی اجتماعی. رئیس بنیادها، مجمع جهانی اقتصاد
اشتراک گذاشتن:
تاثیر ما
مجمع جهانی اقتصاد برای تسریع اقدام در مورد انجمن نهادی چه می کند؟

تصویر بزرگ
بررسی و نظارت بر نحوه نوآوری اجتماعی بر اقتصادها، صنایع و مسائل جهانی تأثیر می گذارد

نوآوری جمع سپاری
مشارکت کنید با پلت فرم دیجیتال جمع سپاری ما برای ارائه تأثیر در مقیاس
به روز بمانید:
دستور کار داووس
Follow
این مقاله بخشی از موارد زیر است:نشست سالانه مجمع جهانی اقتصاد
به مقاله گوش دهید
11 دقیقه گوش دادن
- تنها در اتحادیه اروپا، 2.8 میلیون سازمان اقتصاد اجتماعی وجود دارد که 13.6 میلیون نفر را استخدام می کنند که در برخی کشورها تا 9.9 درصد اشتغال را نشان می دهد.
- اقتصاد اجتماعی از گروه های محروم حمایت می کند، توسعه پایدار را هدایت می کند و جایگزینی برای مدل اقتصادی فعلی ما ارائه می دهد.
- گزارش جدید با عنوان باز کردن قفل اقتصاد اجتماعی، از مجمع جهانی اقتصاد، پنج توصیه کلیدی برای پیشبرد این بخش ارائه می دهد.
همه گیری کووید-19 یک بحران معمولی نبوده است. بدترین وضعیت اضطراری بهداشتی در بیش از یک قرن گذشته با افزایش نابرابری و افزایش سریع قیمت مواد غذایی و انرژی در سال جاری تشدید شده است. این امر باعث آسیب ساختاری به اقتصادها و زندگی مردم در مقیاسی می شود که به سختی می توان با استفاده از رویکردهای سنتی محرک مالی و پولی به آن رسیدگی کرد.
در بسیاری از کشورها، از دست دادن شغل و سایر سختی ها به طور نامتناسبی در میان فقرا، جوانان و زنان متمرکز شده است. در نتیجه، آکسفام گزارش می دهد که تعداد کل افرادی که در فقر شدید هستند می تواند امسال به 860 میلیون نفر افزایش یابد. این امر بر نیاز به مدل های فراگیر توسعه اقتصادی تأکید می کند که انسجام اجتماعی را ایجاد می کند و نابرابری های اجتماعی را برطرف می کند.
خوانده اید؟
در طول دهه ها، شرکت های اجتماعی، تعاونی ها، مشاغل فراگیر و سازمان های غیرانتفاعی نوآورانه، ارزش اجتماعی و زیست محیطی را در اولویت قرار داده اند. آنها در جایی که مهم است تفاوت ایجاد کردند: در زمین، در میان جوامع محلی و اکوسیستم های طبیعی که با آسیب و از دست دادن مواجه هستند. این سازمان ها دارای اهداف اجتماعی صریح و مدل های حکمرانی فراگیر هستند و با گروه هایی کار می کنند که به دلیل جنسیت، نژاد، توانایی و طبقه اقتصادی با موانعی روبرو هستند.
اقتصاد اجتماعی به لطف ریشه های محلی قوی خود، می تواند راه حل های نوآورانه از پایین به بالا برای بسیاری از چالش های جهانی امروز، مانند تغییرات آب و هوایی، دیجیتالی شدن و طرد اجتماعی ارائه دهد. اقتصاد اجتماعی با جوامع محلی و برای آنها کار می کند و پتانسیل ایجاد شغل عظیمی دارد. نیکلاس اشمیت، کمیسر اروپا برای مشاغل و حقوق اجتماعی.
باز کردن قفل اقتصاد اجتماعی
گزارش سازمان ملل تخمین می زند که اقتصاد اجتماعی حدود 7 درصد از تولید ناخالص داخلی جهانی را تشکیل می دهد و به افزایش اشتغال در اقتصادها کمک می کند. در زمان چالش های متعدد و به هم پیوسته، سازمان های اقتصاد اجتماعی جوامع تاب آور را تقویت می کنند و به مدیریت انتقال عمده کمک می کنند. علاوه بر این، اشتغال در اقتصاد اجتماعی در طول بحران مالی سال 2008 12 تا 20 درصد رشد کرد، در مقایسه با از دست دادن شدید شغل در بخش های خصوصی و دولتی.

برای بزرگنمایی کلیک کنید
طیف بازیگران اقتصاد اجتماعی. منبع: مجمع جهانی اقتصاد.
دولت های بیشتری پتانسیل اقتصاد اجتماعی را برای مقابله با چالش های جهانی تشخیص می دهند. امسال کمیسیون اروپا برنامه اقدام اقتصاد اجتماعی خود را راه اندازی کرد. سازمان بین المللی کار برای اولین بار در کنفرانس خود در مورد آن بحث کرده است و سازمان همکاری و توسعه اقتصادی در این زمینه توصیه های قانونی به اعضای خود ارائه می دهد.
اما علیرغم پتانسیل آن، اقتصادهای اجتماعی در سراسر جهان با موانع مشترکی مواجه هستند که مانع از رشد آنها می شود: دید محدود. عدم وجود چارچوب های قانونی و نظارتی حمایتی؛ عدم تأیید و استانداردها؛ عرضه ناکافی منابع مالی و دسترسی محدود به بازارها.
خلاصه بینش، باز کردن قفل اقتصاد اجتماعی، پنج حوزه سیاست گذاری مشخص را تشریح می کند که دولت ها می توانند برای ایجاد جوامع فراگیرتر، پایدارتر و انعطاف پذیرتر توسعه دهند.

برای بزرگنمایی کلیک کنید
حوزه های کلیدی سیاست برای باز کردن قفل اقتصاد اجتماعی. منبع: مجمع جهانی اقتصاد.
1. چارچوب های جدید را بشناسید و بسازید
به رسمیت شناختن سیاسی، توسعه محیط های نظارتی و گفتگوی منظم با بازیگران اقتصاد اجتماعی در کشورها برای رشد این بخش حیاتی است. در سال 2007، جمهوری کره قانون ترویج شرکت های اجتماعی را برای ترویج، تشویق و تنظیم شرکت های اجتماعی وضع کرد. کمیسیون اروپا اخیرا برنامه اقدام اقتصاد اجتماعی 2021-2027 خود را راه اندازی کرده است و بیش از 2.5 میلیارد یورو برای تقویت سرمایه گذاری اجتماعی، حمایت از بازیگران اقتصاد اجتماعی برای راه اندازی، افزایش، نوآوری و ایجاد شغل سرمایه گذاری کرده است.
2. ایجاد مشوق هایی برای تامین مالی و سرمایه گذاری
دولت ها می توانند با سرمایه گذاری بودجه عمومی و تشویق سرمایه گذاری توسط ارائه دهندگان مالی جریان اصلی و سرمایه گذاران اجتماعی، اقتصاد اجتماعی را رشد دهند. مکانیسم ها شامل مشوق های مالی، کاهش موانع نظارتی، استفاده از چارچوب های مالیاتی، ریسک زدایی از بودجه خصوصی و توسعه مکانیسم های ترکیبی است که سرمایه گذاری دولتی و خصوصی را با هم ترکیب می کند. دولت سنگاپور مرکز شرکت های اجتماعی سنگاپور (raiSE) را برای ارائه کمک های مالی به شرکت های اجتماعی مستقر در سنگاپور برای توسعه این بخش و رسیدگی به شکاف های اجتماعی انسان محور در این کشور از طریق همکاری بازیگران دولتی و خصوصی راه اندازی کرد.
3. آموزش و پژوهش را گسترش دهید
گسترش و تقویت تحقیقات و آموزش در زمینه نوآوری اجتماعی، سرمایه گذاری اجتماعی و اقتصاد اجتماعی در مدارس و دانشگاه ها می تواند هم دانش محلی و هم خط لوله استعدادها را توسعه دهد. به عنوان مثال، اسکاتلند برنامه شرکت اجتماعی در آموزش را در سال 2007 برای افزایش درک اقتصاد اجتماعی و ارتقای آگاهی در بین جوانان و دانش آموزان راه اندازی کرد. این برنامه بر توسعه و درک مدل های کسب و کار شرکت های اجتماعی تمرکز دارد و تجربه عملی را ارائه می دهد
کشف
مجمع جهانی اقتصاد برای حمایت از نوآوری اجتماعی چه می کند؟
Show more
کوکی های بازاریابی ما را برای دسترسی به این محتوا بپذیرید.
این کوکی ها در حال حاضر در مرورگر شما غیرفعال هستند.
کوکی ها را بپذیرید
4. کانال های تدارکات عمومی و خصوصی را فراگیرتر کنید
بخش دولتی می تواند کالاها و خدمات را از شرکت هایی خریداری کند که ارزش اجتماعی و زیست محیطی را ارائه می دهند. به این ترتیب، تدارکات به وسیله ای برای دستیابی به اهداف دیگر، مانند ادغام مجدد بیکاران طولانی مدت در بازارهای کار و ادغام اجتماعی و شغلی افراد از گروه های طرد شده یا آسیب پذیر تبدیل می شود. دولت ها همچنین می توانند مشوق هایی را برای بخش خصوصی ایجاد کنند تا از اقتصاد اجتماعی خرید کنند. در سال 2014، کشورهای عضو اتحادیه اروپا قوانین تدارکات عمومی اتحادیه اروپا را تصویب کردند که اجازه می دهد "ملاحظات زیست محیطی و اجتماعی" و همچنین جنبه های نوآوری هنگام اعطای قراردادهای عمومی در نظر گرفته شود.
5. داده های تأثیر اجتماعی را جمع آوری و قابل مشاهده کنید
برای افزایش دید این بخش، دولت ها تشویق می شوند تا آمارهایی را در مورد اقتصاد اجتماعی جمع آوری کنند که فراتر از شاخص های سنتی است. علاوه بر سهم اقتصاد اجتماعی در رشد اقتصادی و ایجاد شغل، دولت ها باید به طور سیستماتیک اثرات اجتماعی و زیست محیطی اقتصاد اجتماعی را اندازه گیری و ارائه دهند. شاخص پیشرفت اجتماعی میزان برآورده شدن نیازهای اجتماعی شهروندان را از طریق سه بعد نیازهای اساسی انسان، پایه های رفاه و فرصت ها با تجمیع 35 شاخص اجتماعی اندازه گیری می کند.
تغییر دوم به سمت تغییر جریان اصلی اقتصاد
بازیگران اقتصاد اجتماعی اغلب در توسعه نوآوری های اجتماعی و زیست محیطی پیشگام هستند. آنها ثابت کرده اند که راه حل هایی را که اقتصاد جریان اصلی اتخاذ کرده است، توسعه می دهند. آنها می توانند با قرار دادن مردم در مرکز، مشارکت های فراگیر و عادلانه ای را در جهت انتقال سبز و دیجیتال به ارمغان بیاورند و می توانند به عنوان منبع الهام بخش خصوصی در اهداف ESG خود عمل کنند.
از آنجایی که مدل های کارآفرینی اجتماعی هم از منظر تأثیر و هم از منظر سود به موفقیت خود ادامه می دهند، بخش خصوصی به طور فزاینده ای شروع به ادغام تأثیر در مدل های عملیاتی خود کرده است، در حالی که همچنان سودآور باقی مانده است. همانطور که این اتفاق می افتد، خطوط بین شرکت های صرفا اجتماعی و شرکت های سنتی که منافع اجتماعی را نیز ایجاد می کنند، به طور فزاینده ای محو می شوند، که چیز خوبی است. شارون تورن ، رئیس هیئت مدیره جهانی Deloitte.
از طریق اتخاذ چارچوب های پاسخگویی، طبقه بندی های گزارشگری اجتماعی، و مدل های تجاری و حاکمیتی مشارکتی تر، اقتصاد اجتماعی می تواند به تحول ساختاری مدل اقتصادی فعلی ما با چالش های مداوم خود کمک کند و انتقال به سمت آینده ای فراگیرتر و پایدارتر را تسریع کند.
گزارش بینش، باز کردن قفل اقتصاد اجتماعی، توسط یک گروه کاری که توسط اتحاد جهانی کارآفرینی اجتماعی مجمع جهانی اقتصاد و بنیاد شواب برای کارآفرینی اجتماعی، با مشارکت Deloitte، Euclid Network، Catalyst 2030 و بنیاد Motsepe تشکیل شده است، ارائه شده است.





































 دانلود فایل برای اعضای دانشگاه
دانلود فایل برای اعضای دانشگاه